NOS R2R simulator
MD5 hash foo_nos_r2r.fb2k-component:
ba369c44a0e08e30221990182150d2b6
ba369c44a0e08e30221990182150d2b6
SHA256 hash foo_nos_r2r.fb2k-component:
7dc6920d67f0db7f1cdc0cb9bae6339e5c5eb96b0c58e4e3fd5e08517d17f853
7dc6920d67f0db7f1cdc0cb9bae6339e5c5eb96b0c58e4e3fd5e08517d17f853
There are two main types of digital-to-analog converter (DAC) architectures for audio today: delta-sigma and R2R. Initially, DAC chips had an R2R architecture, which were later improved by upsampling before the DAC, and then a cheaper and more promising architecture appeared in the form of delta-sigma. Today we are seeing an increase in the popularity of DACs with the original architecture, and in NOS modes (without oversampling).
Some modern delta-sigma DACs offer NOS emulation in their digital filter settings, but the quality of implementation is not always high.
The plugin for foobar2000 was developed as the most complete simulation of an R2R DAC, with the ability to listen through a regular delta-sigma DAC.
Some modern delta-sigma DACs offer NOS emulation in their digital filter settings, but the quality of implementation is not always high.
The plugin for foobar2000 was developed as the most complete simulation of an R2R DAC, with the ability to listen through a regular delta-sigma DAC.
Basic settings
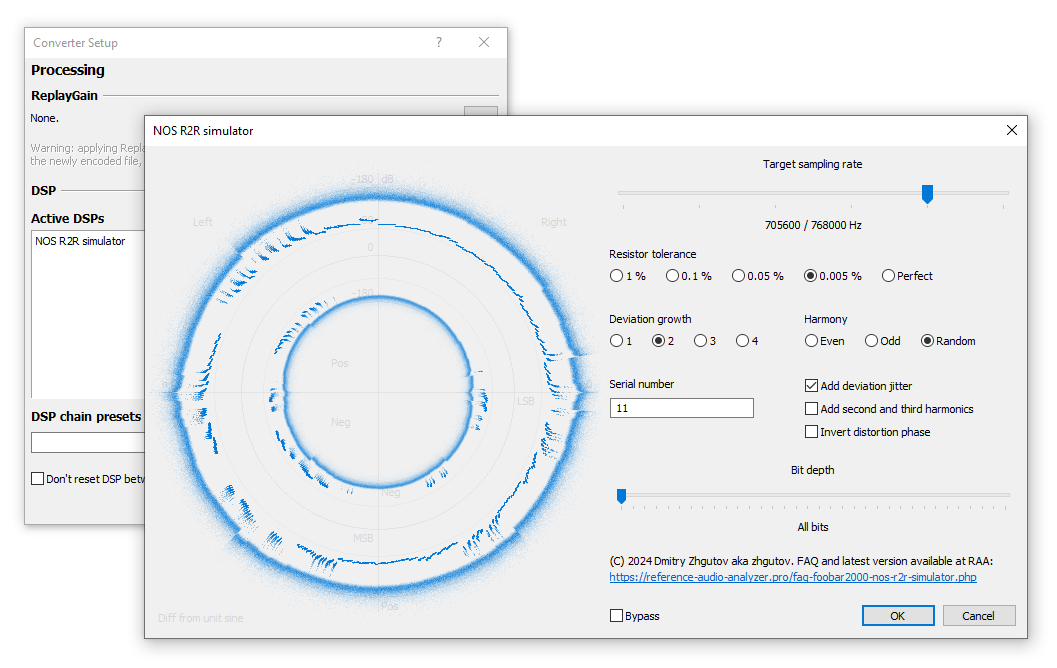
Target sampling rate
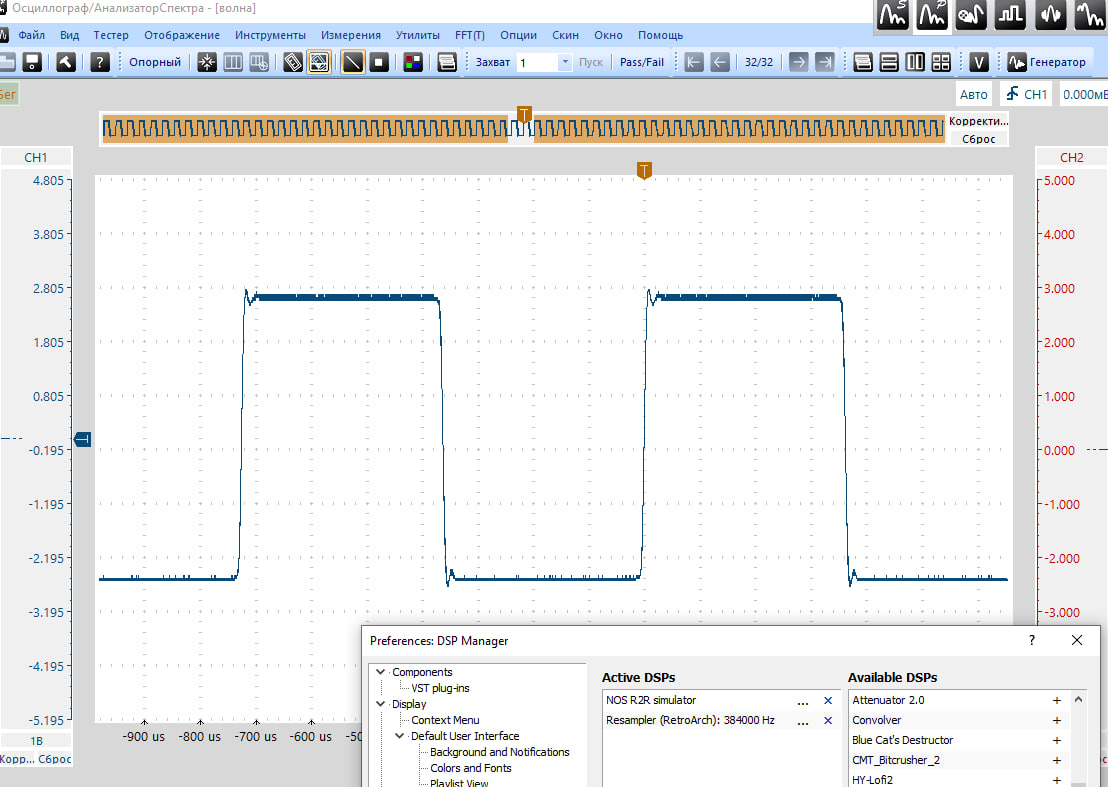
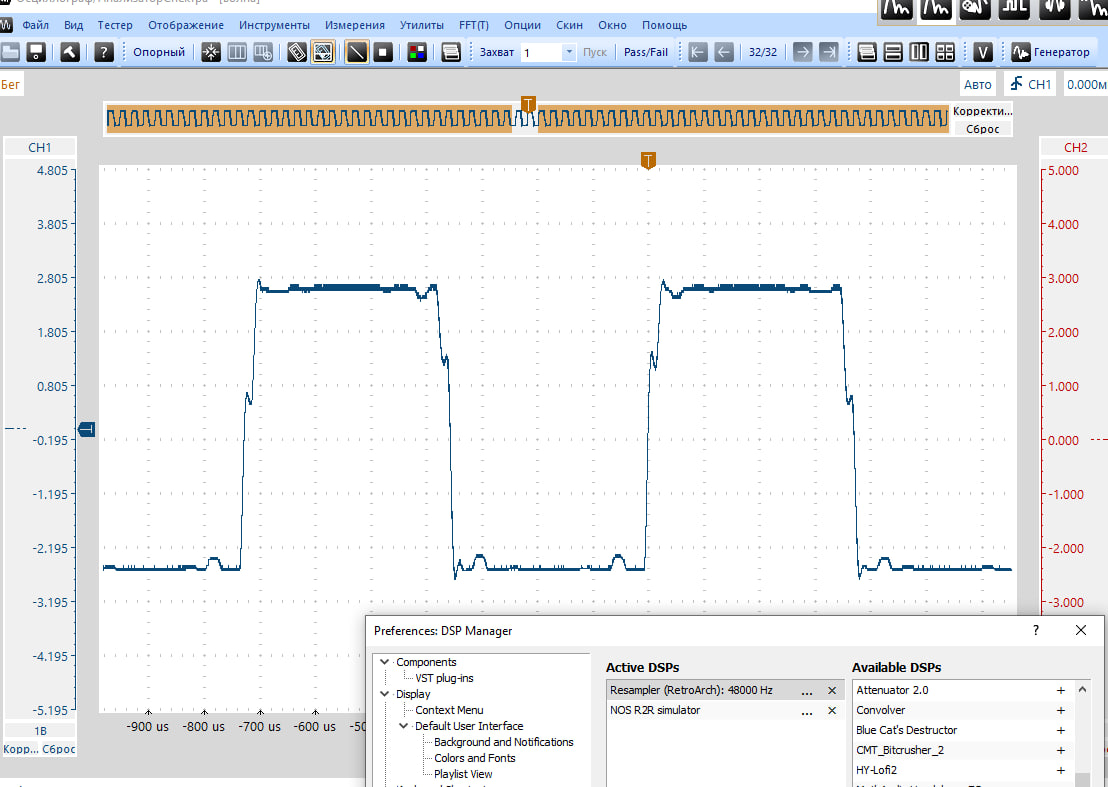
This is a resampler setting that simulates NOS mode. As the frequency increases, the intermediate coordinates simply repeat the value of the previous initial coordinate. If there is playback through a real NOS R2R DAC, then switching frequencies will not affect the signal shape, although the DAC will operate in a different frequency grid.The value sets the maximum frequency at which the resampler will operate.
This means that if a frequency of 705600 Hz is selected, then the original content from 44100, 88200, 176400 or 352800 Hz will be converted to 705600 Hz.
If you select 88200 Hz, then sources from 44100 Hz will be resampled, and everything starting from 88200 Hz will be played back without a resampler at the original frequency.
If you select the first value, equivalent to 44100 Hz, oversampling will be turned off.
RAA makes performance tests for different DAC chips in NOS simulation mode. Currently ready:
- CS43131/43198

- AK4493EQ - EVGA Nu Audio

- AK4493EQ - xDuoo XD-05 Plus

- AK4493EQ - Topping E30

- ES9039 - Topping D90 III

Resistor tolerance
This parameter sets the accuracy of the resistors in the R2R matrix of the DAC. This allows you to hear how the sound changes for the different levels of deviation. The Perfect setting does not introduce the distortion.Deviation growth
This parameter sets the nature of the resistor error deviation in the R2R DAC matrix. Setting 1 assumes that the error is the same across all bits. The higher the setting the faster the deviation increases for the lower bits. This setting emulates the possible error of the resistor switches or other elements, due to which the distortion remains in the region of low amplitudes.Serial number
This is the key that defines the deviations of the resistors. This variable can be any number or word. The error distribution will be the same if you run the plugin in different players with the same value. The example reports use the value "11". You can write in the comments or Telegram which option seems to you the best sounding or similar to the existing R2R DAC implementations.Harmony
Responsible for the error distribution algorithm between the resistors within a series of simulated devices.Random assumes that the resistors are randomly placed in the matrix without special sorting. This corresponds to the microcircuit DACs or the budget assemblies using separate resistors.
When assembled from individual resistors, the manufacturer can make additional distribution of resistors and thereby give the device its own sound character. To emulate this, there are two additional modes: Even - dominance of even harmonics in the spectrum and Odd - dominance of odd harmonics.
The distribution of harmonics can also be influenced by the error of transistor switches and other elements.
A separate page
Random
NOS R2R Simulator 0.1% Odd
NOS R2R Simulator 0.1% Even
Bit depth
Emulates disabling low-order bits. For example, when the DAC matrix is 20-bit, and the audio stream is 24-bit, and when fed to the matrix there is no correct rounding with a dither to 20 bits.Since the audio wave is transmitted symmetrically about the center, the number of levels is not an even number, like 2N, but an odd number, like 2N-1, where the very first level is not used. Thus, for a signal with a width of 2 bits, not four, but only three levels are available, as in 1 bit relative to the center of the wave. If the signal is reduced to 1 bit, then there will be no sound in PCM format.
For 16 bits, accordingly, not 65536, but 65535 levels are available.
In the bit depth settings, 2 bits are designated as 1 bit + sign, and 16 bits as 15 bit + sign.
Add deviation jitter
Adds a small randomness to each resistor activation.Add second and third harmonics
This option simulates the sound of an output stage (or amplifier) working in class A.Random and Odd modes simulate a transistor output stage. The Even mode simulates a tube output stage.
Additional harmonics do not mean that this or that class of amplifier will sound exactly like that. Rather, it is an amplified color of the output stage type for the output power level where the current or voltage amplifier leaves the linear mode in its transfer characteristic
Invert distortion phase
Inverts the phase of distortion and can give a different sound in non-linear paths.Bypass
Disables the plugin.How to listen the simulation not in foobar2000?
You can convert source files into a desired format using foobar2000.In the list of tracks, right-click to open the menu and go to Convert >...
In the conversion settings, select the format (best option is to choose 24 or 32 bit depending on the DAC through which you will listen) and then configure the plugin on the Processing page.
Set the desired settings.
If the device does not support frequencies that are multiples of 44.1 kHz
Is it better to resample from 44.1 kHz to 48 kHz first and then to 384 kHz via the plugin, or vice versa, convert to 352 kHz first with the plugin and then to 384 kHz via resampler?It is better to increase the sampling rate to the maximum possible frequency via plugin, and only then to resample to the frequency supported by your device. In this case, the result will be closer to the perfect NOS emulation.
Subjective sound difference
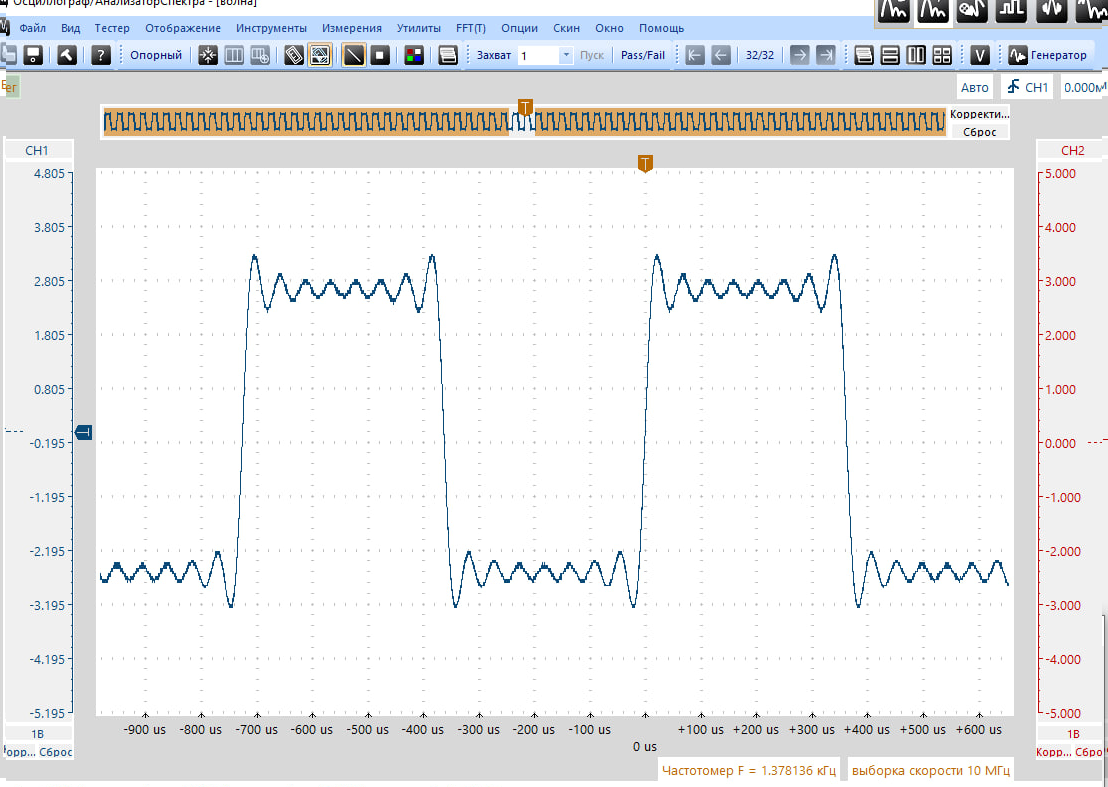
After resampling in NOS emulation, the higher frequencies become reduced and make the sound somewhat softer and less ringing. If you cannot hear this difference, then it is worth checking your hearing or the playback chain.Additionally, NOS emulation gives more intermodulation distortion and here it is a debatable question: if these distortions are audible, then this is a sign of high quality of the path, or vice versa of poor quality.
The main nature of the distortion should be determined by adjusting the parameters of the resistive matrix. If suddenly there is no obvious audibility even at 1%, then you can load several plugins in a row until the sound degradation is absurd, and then, having already understood how exactly the distortions manifest themselves subjectively, try to hear them at lower values.
By analogy with emulators of the tube sound through a transistor amplifier, the emulator can add a tube-like distortion, but cannot remove the effect of the "transistor" sound. Similarly, when playing through a delta-sigma DAC, the effect of NOS R2R will be added, but something from the delta-sigma will inevitably remain.
You can share your impressions in the comments or in Telegram.